
Changes in microtubular polymerization will affect the morphological structure of ER. Reticulons and Dp1/Yop1p proteins do significant role in the stabilization of this sheets and these are the integral proteins helps to form lipid bilayer oligomers. High-curvatures found in the edges of rough ER. The endoplasmic membrane shows the presence of translocon protein which is essential for protein translation takes place in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Large number of sheets form rough ER, they are flattened sac like structures extended in cytoplasm.
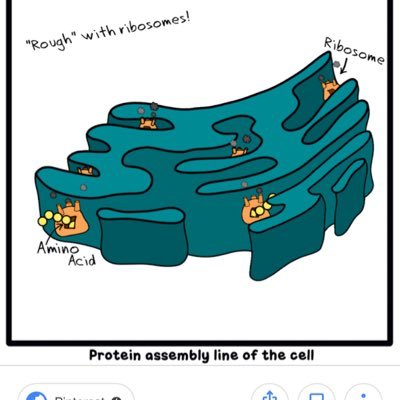
As such the proteins become eligible for the lock and key principle.ER composed of two different morphological features - cisternae and sheets. The proteins taken into the lumen will be modified and folded giving them the basic structural identity.

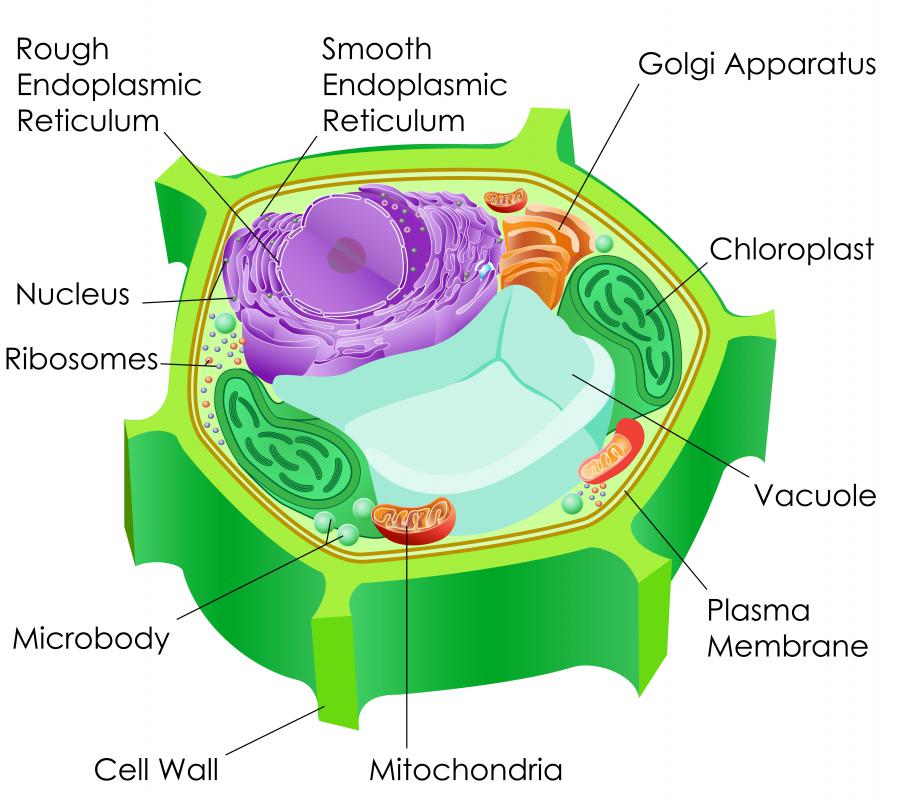
They are made up of flattened convoluted sac-like structures sealed at both their ends. What Does Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Do In A Cell & It’s Definition? As such cell types which are involved in the protein synthesis are rich in rough endoplasmic reticulum and the cell types which are assigned to produce lipids are more in smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Though there are two different types, they appear together and coordinate the cell activities.īasing on the presence and absence of ribosomes on their structure, they are divided into rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum respectively. These are the parts of Biology.īoth these forms are present in both plants and animal cell types. This membrane has its origin from the nucleus.īasing on the function and presence of ribosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum is classified into two types, rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER). It is bilayer in structure i.e., covered by a protective membrane. These tubules collectively modify and produce the proteins and lipids. The endoplasmic reticulum is composed of a group of interconnected sac-like structures called tubules. i.e., tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope. Basically, each structure is composed of three elements. It’s large and dynamic structure assigns several critical roles like calcium storage, lipid (fats) and protein synthesis and their transport and also protein folding. It is a complex and large structure in the cytoplasm and spans between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It is found only in eukaryotes (plants and animal cells) and plays a major role in producing lipids and proteins. Most (50%) of the membrane surface is provided by the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell. What Does The Endoplasmic Reticulum Do And Its Functions? Scanning electron microscopy image showing the structure of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi (G) and Mitochondria (M).

Nucleus, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic reticulum, Ribosomes, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes are examples of cell organelles. They not only serve several functions but also hold the cytoplasm intact. Cell organelles are sub cellular structures which do the compartmentalization and serves different functions. But eukaryotes have well developed cell organelles. The cytoplasm also called as cytosol, maintains and carries out all the vital functions of the cell by means of its organelles.īoth the prokaryotes (primitive forms) and eukaryotes have cell organelles. This facilitates selective absorption of particles in and out of the cell. The bilayer makes it polar at one end and non polar at the other end. Cell membrane is bilayer in nature and is made up of phospholipids. Though there are different cell types (oval, round, cylindrical) they have the same structural organization.Įach cell is lined by a protective outer covering called cell membrane, which holds the fluid called cytoplasm. Each living organism is composed of basic unit of life i.e., the cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
